EGFR Signaling Networks in Cancer Therapy: Unlocking Targeted Treatment Strategies

Cancer, a complex and devastating disease, has emerged as a major healthcare challenge worldwide. Despite significant advances in medical research, the development of effective and tailored therapies remains a pressing need. One crucial area of focus in cancer treatment is targeting specific molecular pathways that drive tumor growth and progression. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling network has gained significant attention in this regard due to its central role in various malignancies.
EGFR Signaling in Cancer
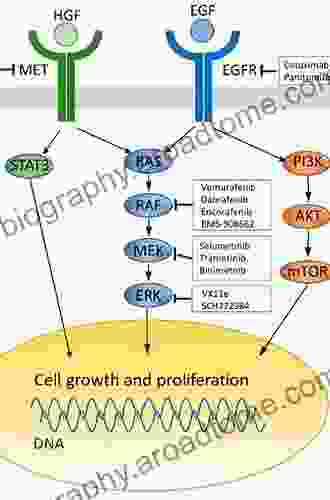
EGFR, a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase, plays a vital role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Dysregulation of EGFR signaling, often resulting from gene amplifications, mutations, or overexpression, has been implicated in the development and progression of a wide range of cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC),head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC),colorectal cancer, and breast cancer.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 25491 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 406 pages |
Upon activation by specific ligands, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) and transforming growth factor alpha (TGFα),EGFR undergoes dimerization and autophosphorylation, leading to the activation of multiple downstream signaling pathways. These pathways include the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway, and the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway, which collectively regulate cellular processes involved in tumorigenesis, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis inhibition, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
EGFR-Targeted Therapies
The central role of EGFR signaling in cancer has made it an attractive therapeutic target. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the development of EGFR-targeted therapies, which offer promising treatment options for patients with EGFR-driven malignancies.
One major class of EGFR-targeted therapies is tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). TKIs are small molecules that competitively bind to the ATP-binding pocket of EGFR, thereby inhibiting its kinase activity and downstream signaling. Gefitinib, erlotinib, and afatinib are examples of first-generation TKIs that have shown efficacy in treating EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Second-generation TKIs, such as dacomitinib and osimertinib, have improved potency and selectivity, making them effective in overcoming resistance to first-generation TKIs.
Another class of EGFR-targeted therapies is monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). mAbs are designed to bind to specific epitopes on the extracellular domain of EGFR, thereby blocking ligand binding and subsequent receptor activation. Cetuximab and panitumumab are examples of EGFR-targeting mAbs that have demonstrated clinical benefit in treating HNSCC and colorectal cancer, respectively.
Combination Therapies
While EGFR-targeted therapies have shown promising results, the development of resistance remains a significant challenge. To overcome resistance and enhance therapeutic efficacy, combination therapies involving EGFR-targeted agents and other therapeutic modalities have been explored.
One approach is combining EGFR TKIs with cytotoxic chemotherapy. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that the combination of TKIs and chemotherapy can improve tumor regression and survival compared to either therapy alone. Additionally, combining EGFR TKIs with other targeted therapies, such as BRAF inhibitors or MEK inhibitors, has shown promising results in treating patients with specific genetic alterations.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has emerged as a powerful treatment modality for cancer, and its combination with EGFR-targeted therapies has shown promising results. Immunotherapy involves harnessing the patient's own immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. By combining EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as PD-1 or CTLA-4 inhibitors, the immune system can be further activated to enhance antitumor responses.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Research into EGFR signaling networks in cancer therapy is an active and rapidly evolving field. Ongoing studies are focused on further understanding the molecular mechanisms of EGFR-driven tumorigenesis, identifying novel therapeutic targets, developing more potent and selective EGFR inhibitors, and optimizing combination therapies to improve patient outcomes.
One promising area of research is the development of allosteric EGFR inhibitors, which target different conformations of the receptor compared to conventional TKIs. Allosteric inhibitors have the potential to overcome resistance and expand the therapeutic window of EGFR-targeted therapies.
Another area of focus is the identification of predictive biomarkers that can guide patient selection for EGFR-targeted therapies and predict response to treatment. By understanding the molecular characteristics of tumors that respond well to EGFR inhibition, clinicians can tailor treatment decisions to maximize therapeutic benefit.
EGFR signaling networks play a crucial role in cancer development and progression. Targeting EGFR with specific inhibitors has revolutionized the treatment of EGFR-driven malignancies, offering promising therapeutic options for patients. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of EGFR signaling, leading to the development of novel therapeutic strategies and combination therapies that aim to improve patient outcomes and advance the fight against cancer.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 25491 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 406 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Kevin Candela
Kevin Candela Parkinson S Foundation
Parkinson S Foundation Joe Keohane
Joe Keohane S L Bridle
S L Bridle Weixun Wang
Weixun Wang Oliver Montenbruck
Oliver Montenbruck Michel Biron
Michel Biron Douglas W Carpenter Psy D
Douglas W Carpenter Psy D Seth Lerer
Seth Lerer Sam Key
Sam Key Olusoji Adeyi
Olusoji Adeyi Faizun Kamal
Faizun Kamal Abhinav Prakash
Abhinav Prakash David Ronka
David Ronka Nika La Valentina
Nika La Valentina Ernest Bartels
Ernest Bartels Katie Singer
Katie Singer Karen Ager
Karen Ager Corey Charles
Corey Charles Hayden Finch Phd
Hayden Finch Phd
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Cormac McCarthyRevise SQE Property Law and Practice: Your Essential Guide to Success in the...
Cormac McCarthyRevise SQE Property Law and Practice: Your Essential Guide to Success in the... Martin CoxFollow ·15.8k
Martin CoxFollow ·15.8k Nathaniel PowellFollow ·12.3k
Nathaniel PowellFollow ·12.3k Craig CarterFollow ·4k
Craig CarterFollow ·4k Ashton ReedFollow ·11k
Ashton ReedFollow ·11k George HayesFollow ·16.6k
George HayesFollow ·16.6k Michael SimmonsFollow ·15.1k
Michael SimmonsFollow ·15.1k Casey BellFollow ·14.3k
Casey BellFollow ·14.3k Brenton CoxFollow ·18.4k
Brenton CoxFollow ·18.4k
 Ashton Reed
Ashton ReedUnveiling the Silent Pandemic: Bacterial Infections and...
Bacterial infections represent...

 Brent Foster
Brent FosterFinally, Outcome Measurement Strategies Anyone Can...
In today's...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsUnlocking the Secrets to Entrepreneurial Excellence:...
Empowering...

 Eugene Powell
Eugene PowellOur Search For Uncle Kev: An Unforgettable Journey...
Prepare to be captivated by...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 25491 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 406 pages |