Unveiling the Silent Pandemic: Bacterial Infections and their Devastating Toll on Humanity

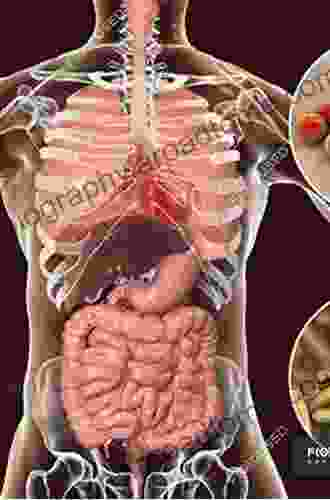
Bacterial infections represent a formidable threat to global health, silently plaguing humanity for centuries. These microscopic organisms, lurking within our bodies and the environment, have the potential to cause a vast spectrum of diseases, from mild respiratory ailments to life-threatening sepsis. Understanding the epidemiology and control of bacterial infections is fundamental to safeguarding public health and minimizing their devastating impact.
Epidemiology of Bacterial Infections
The burden of bacterial infections is staggering. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that bacterial infections are responsible for over seven million deaths annually, accounting for nearly 13% of all deaths worldwide. These infections can strike individuals of all ages and demographics, with young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals being particularly susceptible.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 8311 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1002 pages |
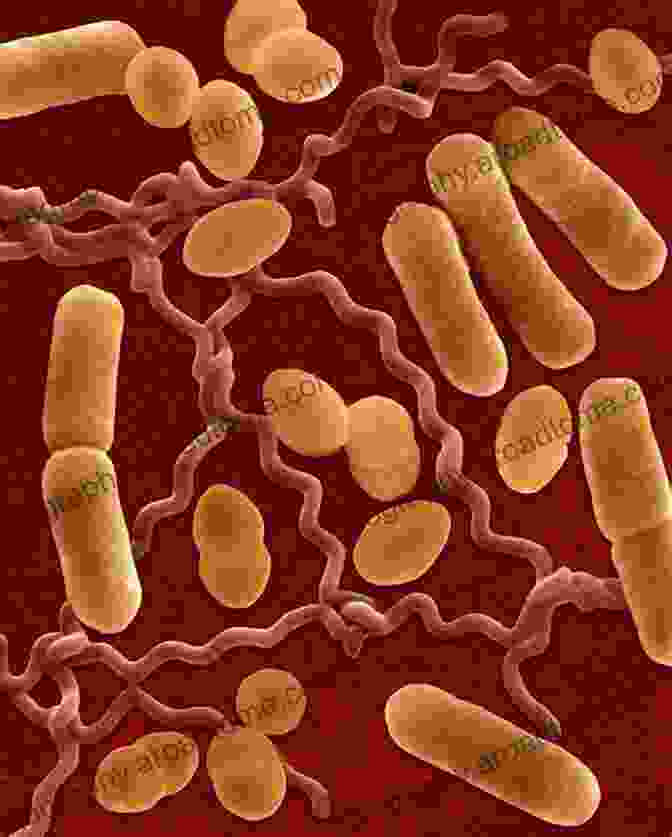
Bacterial infections are ubiquitous, affecting both developed and developing countries. In developing countries, where sanitation and healthcare access are often limited, bacterial infections such as pneumonia, diarrhoea, and tuberculosis remain major causes of morbidity and mortality. In developed countries, while the overall burden of bacterial infections is lower, the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains has become a growing concern.
Clinical Manifestations of Bacterial Infections
The clinical manifestations of bacterial infections are as diverse as the bacteria themselves. Some bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, commonly cause respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia and meningitis. Others, like Staphylococcus aureus, are notorious for causing skin and soft tissue infections, including boils, abscesses, and even life-threatening sepsis.
Certain bacteria, such as Helicobacter pylori, have a predilection for specific organs. H. pylori is the primary cause of peptic ulcer disease, a common condition that affects the lining of the stomach and duodenum. Other bacteria, like Mycobacterium tuberculosis, are highly specialized and cause specific diseases, such as tuberculosis.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Bacterial infections can be transmitted through various routes, including airborne droplets, direct contact, contaminated food or water, and animal bites. Understanding the specific transmission mechanisms of different bacteria is essential for developing effective control measures.
Risk factors for bacterial infections vary depending on the pathogen. Factors such as age, immune status, underlying medical conditions, and lifestyle choices can all influence an individual's susceptibility to infection. For instance, people with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or receiving immunosuppressive therapy, are at an increased risk of developing serious bacterial infections.
Control and Prevention of Bacterial Infections
Controlling and preventing bacterial infections require a multifaceted approach that involves both individual and public health measures. Effective strategies include:
Hand Hygiene:
Maintaining proper hand hygiene is one of the most important ways to prevent the spread of bacterial infections. Regular handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Vaccination:
Vaccines play a crucial role in protecting individuals from specific bacterial infections. Vaccines are available for a variety of bacterial pathogens, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and Neisseria meningitidis.
Antibiotic Stewardship:
Antibiotics are powerful tools in combating bacterial infections. However, their overuse and misuse can lead to the emergence of antibiotic resistance, a growing threat to public health. Antibiotic stewardship programs aim to ensure that antibiotics are used appropriately and effectively, minimizing the development of resistance.
Surveillance and Outbreak Control:
Surveillance systems are essential for tracking the incidence and spread of bacterial infections. Rapid detection and timely response to outbreaks can help contain the spread of infection and prevent further cases.
Environmental Control:
Environmental control measures, such as proper sanitation, clean water supplies, and food safety practices, play a vital role in reducing the transmission of bacterial infections. Adequate sanitation facilities and access to clean drinking water are particularly important in resource-limited settings.
Bacterial infections remain a significant global health threat, claiming millions of lives annually. Understanding the epidemiology and control of these infections is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By implementing comprehensive control measures, including hand hygiene, vaccination, antibiotic stewardship, surveillance, and environmental control, we can minimize the impact of bacterial infections and safeguard the health of our communities.
Further research is needed to develop new diagnostic tools, antibiotics, and vaccines to combat the ever-evolving threat of bacterial infections. By investing in research and promoting public health education, we can create a future where these silent pandemic no longer poses a devastating threat to humanity.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 8311 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1002 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Raji Swaminathan
Raji Swaminathan Sidney Greidanus
Sidney Greidanus Carey Newman
Carey Newman Pam Peters
Pam Peters Melanie Morse
Melanie Morse John Milton Gregory
John Milton Gregory Katie Halliwell
Katie Halliwell Sean Webb
Sean Webb Chester Smith
Chester Smith Sheldon X D Tan
Sheldon X D Tan David Palting
David Palting H Jon Benjamin
H Jon Benjamin Christine Chaundler
Christine Chaundler Ronald S Jackson
Ronald S Jackson Mark A Gabriel
Mark A Gabriel George Mccloskey
George Mccloskey Carolyn A Dehlinger
Carolyn A Dehlinger Theoni Pappas
Theoni Pappas David Owen
David Owen Andrea Q Robinson
Andrea Q Robinson
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Forrest ReedUnveiling the True Story of the Shimabara Rebellion: A Captivating Chronicle...
Forrest ReedUnveiling the True Story of the Shimabara Rebellion: A Captivating Chronicle... James HayesFollow ·18.5k
James HayesFollow ·18.5k Jesus MitchellFollow ·7.2k
Jesus MitchellFollow ·7.2k Howard BlairFollow ·17.5k
Howard BlairFollow ·17.5k Enrique BlairFollow ·14.1k
Enrique BlairFollow ·14.1k Gerald ParkerFollow ·2.9k
Gerald ParkerFollow ·2.9k Winston HayesFollow ·4k
Winston HayesFollow ·4k Art MitchellFollow ·13.6k
Art MitchellFollow ·13.6k Jamie BlairFollow ·14.6k
Jamie BlairFollow ·14.6k
 Ashton Reed
Ashton ReedUnveiling the Silent Pandemic: Bacterial Infections and...
Bacterial infections represent...

 Brent Foster
Brent FosterFinally, Outcome Measurement Strategies Anyone Can...
In today's...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsUnlocking the Secrets to Entrepreneurial Excellence:...
Empowering...

 Eugene Powell
Eugene PowellOur Search For Uncle Kev: An Unforgettable Journey...
Prepare to be captivated by...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 8311 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1002 pages |