Indoor Air Pollution: The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 64

5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2972 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 348 pages |
| Paperback | : | 124 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 8.5 ounces |
| Dimensions | : | 6 x 0.31 x 9 inches |
: The Silent Threat
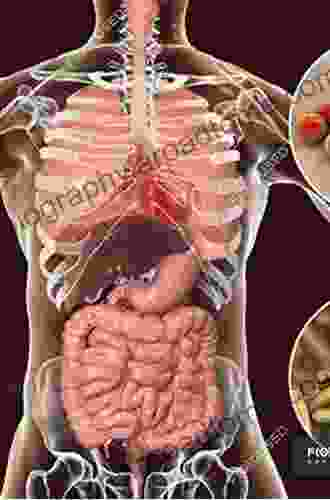
We spend a significant portion of our lives indoors, which makes the quality of indoor air crucial to our overall well-being. Yet, we often overlook the potential hazards lurking within our homes, schools, and workplaces.
Indoor air pollution is a serious but often overlooked environmental health issue. It refers to the presence of various pollutants in indoor air that can adversely affect our health. These pollutants can originate from a wide range of sources, including building materials, furnishings, cleaning products, and human activities.
Health Effects of Indoor Air Pollution
Exposure to indoor air pollutants can have a range of adverse health effects, from mild discomfort to severe respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses. Some common health problems associated with indoor air pollution include:
- Respiratory problems (e.g., asthma, allergies, bronchitis)
- Cardiovascular issues (e.g., heart disease, stroke)
- Neurological disFree Downloads (e.g., headaches, memory loss, fatigue)
- Cancer (e.g., lung cancer, leukemia)
Sources of Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution can stem from various sources, including:
- Building materials: Construction materials like drywall, insulation, and flooring can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air.
- Furnishings: Furniture, carpets, and curtains can emit VOCs and other pollutants.
- Cleaning products: Harsh chemicals found in cleaning products contribute to indoor air pollution.
- Combustion: Burning gas appliances, fireplaces, and tobacco products releases pollutants into the air.
- Human activities: Cooking, showering, and smoking can generate pollutants.
Mitigation Strategies for Indoor Air Pollution
Effectively reducing indoor air pollution requires a multifaceted approach. Some effective mitigation strategies include:
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation by opening windows or using mechanical systems helps to remove pollutants from the air.
- Air purification: Air purifiers with HEPA filters can remove airborne particles and pollutants.
- Source control: Identifying and eliminating sources of pollution (e.g., VOC-emitting materials) can significantly reduce indoor air pollution.
- Green building practices: Incorporating sustainable materials and design principles during construction can minimize indoor air pollution.
- Lifestyle changes: Simple changes, such as avoiding smoking indoors or using low-VOC cleaning products, can reduce exposure to pollutants.
The Role of the Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 64
The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 64: Indoor Air Pollution provides a comprehensive overview of the latest research and advancements in the field of indoor air quality. This invaluable resource offers:
- Detailed analysis of indoor air pollutants, their sources, and health effects
- State-of-the-art research on mitigation strategies and best practices
- Best practices for air quality monitoring and assessment
- Case studies and real-world examples of successful indoor air quality management
Indoor air pollution poses a significant threat to our health and well-being. However, by armed with the knowledge provided in the Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 64, we can take proactive steps to mitigate indoor air pollution and create healthier indoor environments. This comprehensive guide empowers readers with the latest scientific research, effective strategies, and real-world examples to safeguard their health and enhance the quality of their indoor air.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2972 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 348 pages |
| Paperback | : | 124 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 8.5 ounces |
| Dimensions | : | 6 x 0.31 x 9 inches |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Catherine Marshall
Catherine Marshall Thomas D Taylor
Thomas D Taylor Kathy Seaman Shaw
Kathy Seaman Shaw Patricia Horton
Patricia Horton Rumisha Motilal
Rumisha Motilal Lynne Robitaille
Lynne Robitaille R S Yeoman
R S Yeoman Peter Jones
Peter Jones Nahid Siamdoust
Nahid Siamdoust William R Miller
William R Miller Dan Formosa
Dan Formosa Lindsay Goldwert
Lindsay Goldwert Jason R Rich
Jason R Rich Bex Lewis
Bex Lewis Joni Ernst
Joni Ernst Gerald Posner
Gerald Posner Chris Miller
Chris Miller Asad Bashey
Asad Bashey William Lane Craig
William Lane Craig Benjamin Hirsch
Benjamin Hirsch
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Demetrius CarterUnlock the Power of Fiber for Weight Loss with "High Fiber Weight Loss" by...
Demetrius CarterUnlock the Power of Fiber for Weight Loss with "High Fiber Weight Loss" by...
 Frank MitchellUnveiling the Hidden Wonders: Karstological Railway Planning in Slovenia—Cave...
Frank MitchellUnveiling the Hidden Wonders: Karstological Railway Planning in Slovenia—Cave... Levi PowellFollow ·14.5k
Levi PowellFollow ·14.5k Jack LondonFollow ·5.3k
Jack LondonFollow ·5.3k Alexander BlairFollow ·3.5k
Alexander BlairFollow ·3.5k Boris PasternakFollow ·3.5k
Boris PasternakFollow ·3.5k Fernando PessoaFollow ·12.1k
Fernando PessoaFollow ·12.1k John UpdikeFollow ·18.1k
John UpdikeFollow ·18.1k Adam HayesFollow ·17.2k
Adam HayesFollow ·17.2k Charlie ScottFollow ·11.5k
Charlie ScottFollow ·11.5k
 Ashton Reed
Ashton ReedUnveiling the Silent Pandemic: Bacterial Infections and...
Bacterial infections represent...

 Brent Foster
Brent FosterFinally, Outcome Measurement Strategies Anyone Can...
In today's...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsUnlocking the Secrets to Entrepreneurial Excellence:...
Empowering...

 Eugene Powell
Eugene PowellOur Search For Uncle Kev: An Unforgettable Journey...
Prepare to be captivated by...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2972 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 348 pages |
| Paperback | : | 124 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 8.5 ounces |
| Dimensions | : | 6 x 0.31 x 9 inches |