Unleashing the Power of Nature: Enzymatic and Microbial Tools for Sustainable Bioethanol Production

In the face of dwindling fossil fuel reserves and the pressing need for cleaner energy sources, bioethanol has emerged as a promising alternative. This renewable fuel, produced from plant biomass, offers a sustainable solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. At the heart of efficient bioethanol production lies the power of enzymes and microbes, providing innovative tools to harness the potential of biomass and unlock its energy-rich content.
Enzymes: Nature's Biological Catalysts
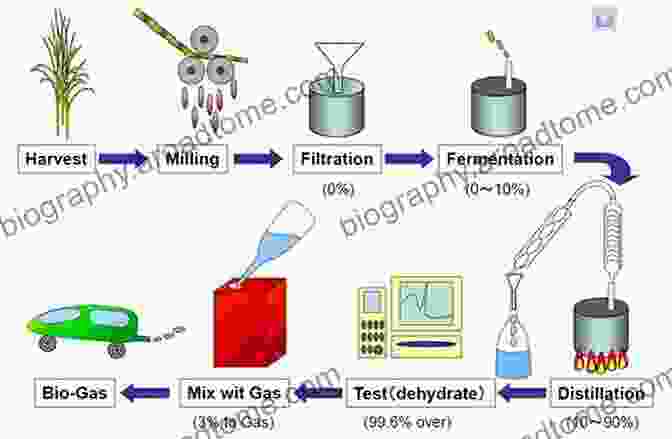
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions, accelerating the conversion of substrates into desired products. They play a crucial role in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, such as cellulose and starch, into fermentable sugars. Cellulases and hemicellulases are key enzymes involved in this process, breaking down the tough cell walls of plant biomass to release the fermentable sugars.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 1189 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 214 pages |
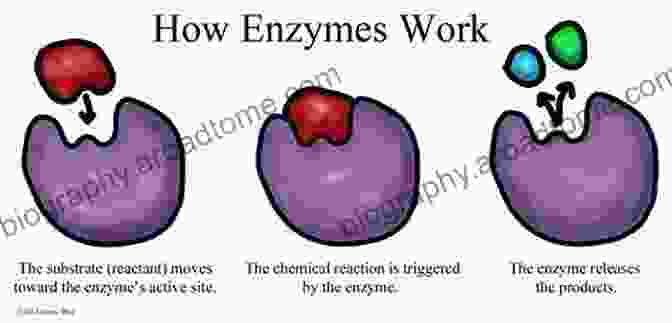
Harnessing Microbial Power
Microorganisms, including yeast and bacteria, are essential partners in bioethanol production. Yeast, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, convert fermentable sugars into ethanol through the process of fermentation. Bacteria, like Zymomonas mobilis, offer unique advantages in ethanol production, exhibiting high ethanol tolerance and efficient sugar utilization.
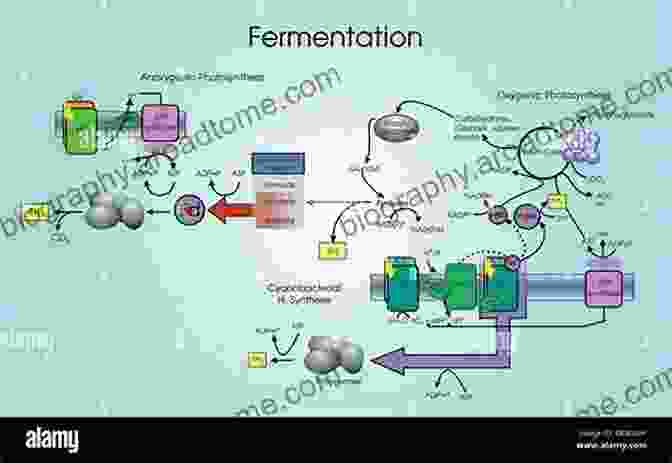
Synergistic Enzyme-Microbial Interactions
The combination of enzymes and microbes creates a powerful synergy that enhances bioethanol production. Enzymes break down the complex structure of biomass, releasing fermentable sugars. These sugars are then efficiently converted into ethanol by microbes. This synergistic interaction optimizes the entire process, maximizing ethanol yield and reducing production costs.
Challenges and Advancements
Despite the potential of enzymes and microbes in bioethanol production, challenges remain. The high cost of enzyme production and the need for efficient microbial strains pose barriers to widespread implementation. Ongoing research focuses on developing cost-effective enzymes, engineering robust microbes, and optimizing the enzyme-microbe interplay to improve bioethanol production efficiency.
Practical Applications
The advancements in enzymatic and microbial tools have led to practical applications in bioethanol production facilities worldwide. These tools enable the efficient breakdown of various biomass sources, including agricultural residues, energy crops, and even waste materials. The resulting bioethanol is blended with gasoline to produce renewable transportation fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable energy systems.
Environmental Impact
Bioethanol production using enzymatic and microbial tools offers significant environmental benefits. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Additionally, the use of sustainable biomass sources promotes carbon sequestration, further mitigating climate change impacts.
Future Outlook
The future of bioethanol production is promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements. The development of new enzyme and microbial technologies, coupled with process optimization, holds the potential to make bioethanol even more competitive with conventional fuels. The transition to bioethanol-based transportation systems will contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Enzymatic and microbial tools have revolutionized bioethanol production, providing efficient and sustainable means to harness the energy potential of biomass. The collaborative action of enzymes and microbes breaks down complex carbohydrates, unlocking the fermentable sugars necessary for ethanol production. As research and innovation continue, the future of enzymatic and microbial tools in bioethanol production holds exciting possibilities for a greener, more sustainable energy landscape.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 1189 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 214 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Gustave Courbet
Gustave Courbet Tanushree Podder
Tanushree Podder Kathrin Zenkina
Kathrin Zenkina Sue Barber Westin
Sue Barber Westin Steven Quay
Steven Quay David Vine
David Vine Shelby Jean Roberson Bender
Shelby Jean Roberson Bender Leo Cullum
Leo Cullum Ethan Quinn
Ethan Quinn Lindsay Goldwert
Lindsay Goldwert Chad Marks
Chad Marks Matthew Cantello
Matthew Cantello Scott Matthews
Scott Matthews Marios Loukas
Marios Loukas Eavan Boland
Eavan Boland Steven Melin
Steven Melin Mario Gheras
Mario Gheras Duncan Leigh
Duncan Leigh 2nd Edition Kindle Edition With Audio Video
2nd Edition Kindle Edition With Audio Video Dmitry I Ignatov
Dmitry I Ignatov
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Wesley ReedUnveiling the Enchanting Realm of "The Beautiful Unseen": A Literary Journey...
Wesley ReedUnveiling the Enchanting Realm of "The Beautiful Unseen": A Literary Journey... Samuel BeckettFollow ·16.2k
Samuel BeckettFollow ·16.2k Julio Ramón RibeyroFollow ·16.1k
Julio Ramón RibeyroFollow ·16.1k Alexander BlairFollow ·3.5k
Alexander BlairFollow ·3.5k Bernard PowellFollow ·15.6k
Bernard PowellFollow ·15.6k Camden MitchellFollow ·8.7k
Camden MitchellFollow ·8.7k Evan HayesFollow ·6.5k
Evan HayesFollow ·6.5k Donald WardFollow ·5.9k
Donald WardFollow ·5.9k Javier BellFollow ·15.8k
Javier BellFollow ·15.8k
 Ashton Reed
Ashton ReedUnveiling the Silent Pandemic: Bacterial Infections and...
Bacterial infections represent...

 Brent Foster
Brent FosterFinally, Outcome Measurement Strategies Anyone Can...
In today's...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsUnlocking the Secrets to Entrepreneurial Excellence:...
Empowering...

 Eugene Powell
Eugene PowellOur Search For Uncle Kev: An Unforgettable Journey...
Prepare to be captivated by...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 1189 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 214 pages |