Neuroimaging of Traumatic Brain Injury: Exploring the Hidden Damage

Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide each year. TBI can result from a variety of causes, including motor vehicle accidents, sports injuries, and falls. The severity of TBI can range from mild to severe, and the consequences can be lifelong.
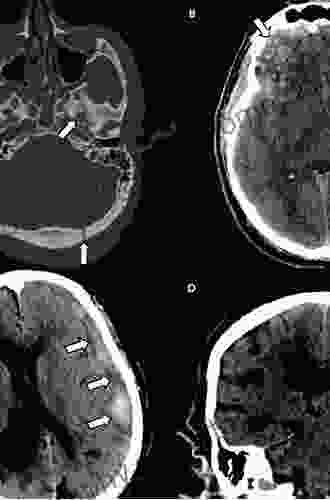
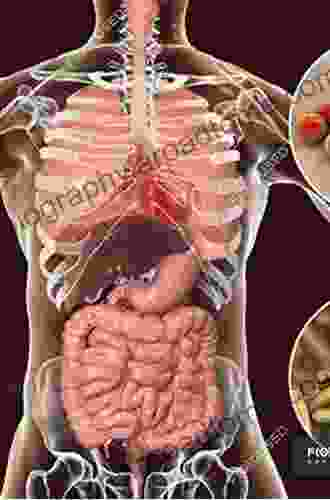
Neuroimaging plays a critical role in the diagnosis and management of TBI. Neuroimaging techniques can help to identify the location and extent of brain injury, as well as to assess the severity of the injury and to monitor its progression.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in neuroimaging techniques for TBI. These advancements have led to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of TBI and have improved the diagnosis and management of this condition.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10318 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 261 pages |
A variety of neuroimaging techniques can be used to evaluate TBI. The most commonly used techniques include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. MRI is the most sensitive neuroimaging technique for detecting TBI, and it can be used to identify even small areas of brain injury.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain. CT is less sensitive than MRI for detecting TBI, but it is faster and less expensive.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to measure brain activity. PET can be used to identify areas of the brain that are injured or dysfunctional after TBI.
- Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a nuclear medicine imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to measure brain blood flow. SPECT can be used to identify areas of the brain that are injured or dysfunctional after TBI.
- Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. fMRI can be used to identify areas of the brain that are activated during different tasks, and it can be used to assess the effects of TBI on brain function.
- Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that measures the diffusion of water molecules in the brain. DTI can be used to identify areas of the brain that are injured or dysfunctional after TBI, and it can be used to track the progression of TBI over time.
- Tractography is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses DTI to map the white matter tracts in the brain. Tractography can be used to identify areas of the brain that are injured or dysfunctional after TBI, and it can be used to track the progression of TBI over time.
Neuroimaging biomarkers are objective measures that can be used to identify and quantify TBI. Neuroimaging biomarkers can be used to:
- Diagnose TBI
- Assess the severity of TBI
- Monitor the progression of TBI
- Predict the outcome of TBI
A number of neuroimaging biomarkers have been identified for TBI. These biomarkers include:
- Brain volume
- White matter integrity
- Gray matter density
- Cerebral blood flow
- Brain metabolism
Neuroimaging biomarkers are a valuable tool for the diagnosis and management of TBI. These biomarkers can help to improve the accuracy of TBI diagnosis, assess the severity of TBI, monitor the progression of TBI, and predict the outcome of TBI.
Neuroimaging plays a critical role in the diagnosis and management of TBI. Neuroimaging techniques can help to identify the location and extent of brain injury, assess the severity of the injury, monitor its progression, and predict its outcome.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in neuroimaging techniques for TBI. These advancements have led to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of TBI and have improved the diagnosis and management of this condition.
Neuroimaging biomarkers are objective measures that can be used to identify and quantify TBI. Neuroimaging biomarkers can be used to diagnose TBI, assess its severity, monitor its progression, and predict its outcome.
Neuroimaging biomarkers are a valuable tool for the diagnosis and management of TBI. These biomarkers can help to improve the accuracy of TBI diagnosis, assess the severity of TBI, monitor the progression of TBI, and predict the outcome of TBI.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10318 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 261 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Jeffrey S Reber
Jeffrey S Reber Hannah J Stolze
Hannah J Stolze Genevieve Lester
Genevieve Lester Rick Canton
Rick Canton Saray Stancic
Saray Stancic Laura Seftel
Laura Seftel Matt Wiley
Matt Wiley R D Martin
R D Martin Larry Fleetwood Jr
Larry Fleetwood Jr 2nd Edition
2nd Edition Kim Diehl
Kim Diehl Erma Bombeck
Erma Bombeck Chris Stricklin
Chris Stricklin Patrick Heron
Patrick Heron Forrest L Richardson
Forrest L Richardson David Barton
David Barton Gustave Courbet
Gustave Courbet Yong Bai
Yong Bai Ann Ingle
Ann Ingle Brad Kelln
Brad Kelln
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 DeShawn PowellWhen America First Met China: Unveiling the Tapestry of Diplomatic Encounters
DeShawn PowellWhen America First Met China: Unveiling the Tapestry of Diplomatic Encounters
 Richard SimmonsUnlock the Secrets of Ancient Greece with "The Teacher's Notes to Reading...
Richard SimmonsUnlock the Secrets of Ancient Greece with "The Teacher's Notes to Reading... Shaun NelsonFollow ·2.8k
Shaun NelsonFollow ·2.8k Raymond ParkerFollow ·14.6k
Raymond ParkerFollow ·14.6k Emmett MitchellFollow ·18.9k
Emmett MitchellFollow ·18.9k Jeffrey CoxFollow ·5.9k
Jeffrey CoxFollow ·5.9k Carson BlairFollow ·18.1k
Carson BlairFollow ·18.1k Bruce SnyderFollow ·10.3k
Bruce SnyderFollow ·10.3k Harry HayesFollow ·19.9k
Harry HayesFollow ·19.9k Jay SimmonsFollow ·13.8k
Jay SimmonsFollow ·13.8k
 Ashton Reed
Ashton ReedUnveiling the Silent Pandemic: Bacterial Infections and...
Bacterial infections represent...

 Brent Foster
Brent FosterFinally, Outcome Measurement Strategies Anyone Can...
In today's...

 Brett Simmons
Brett SimmonsUnlocking the Secrets to Entrepreneurial Excellence:...
Empowering...

 Eugene Powell
Eugene PowellOur Search For Uncle Kev: An Unforgettable Journey...
Prepare to be captivated by...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10318 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 261 pages |